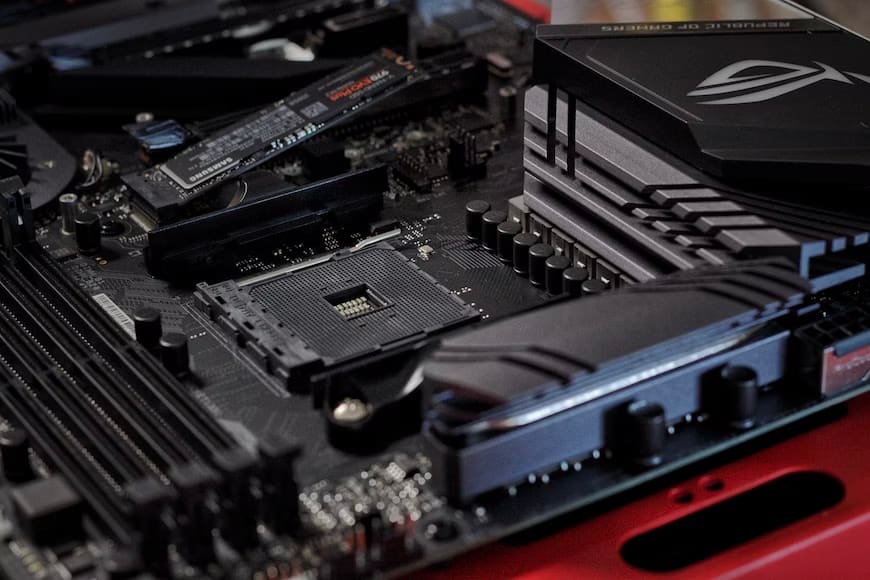
To choose the right motherboard for your PC build, you must check its chipset compatibility with the processor and other peripherals. As every component of your PC directly gets plugged into the motherboard, its form factor and socket compatibility determine what type of performance and features you will get per your need and budget.
While choosing the motherboard, you ensure that it must be ready to meet your current and future requirements. From upgrade & overclocking functionalities to expansion slots and the number of ports, there are a lot of crucial specs you must consider, which I have covered in this guide. Let’s see.
Features to Consider
These are some crucial specs and factors that will help you pick the right motherboard:
1. Chipset Type & CPU Compatibility
Firstly, you must always check your motherboard chipset compatibility with the processor. Both motherboard and CPU must be of the same manufacturer for compatibility. You cannot use an Intel CPU with an AMD motherboard and vice versa.
Ideally, you should first choose a CPU for the new PC build per your needs and budget and then look for a motherboard having a compatible socket and overclocking abilities for your processor.
Depending upon which generation processor you choose, the motherboard’s socket type and chipset vary like this:
For Intel:
| Motherboard Socket Type | Supported CPU Generation | Chipsets |
|---|---|---|
| LGA 1700 | 12th Gen | Alder Lake (12th-gen): H610, B660, H670, Q670, Z690, W680 |
| LGA 1200 | 10th & 11th Gen | For 11th Gen: RocketLake H510, B560, H570, Q570, Z590, W580 For 10th Gen: Comet Lake H410, B460, H470, Q470, Z490, W480 |
| LGA 1151 | 8th and 9th Gen | For 9th Gen: Coffee Lake Z390, B365, B360 For 8th Gen: Coffee Lake H310, B360, H370, Q370, Z370 |
| LGA 2066 | Kaby Lake-X/ Skylake-X | X299 |
For AMD:
| Motherboard Socket Type | Supported CPU Generation | Chipsets |
|---|---|---|
| AM4 | Athlon, AMD Ryzen, 7th-Gen A series | A300, A320, B350, B450, X370, X470, X570 |
| AM5 | AMD Ryzen 4th Gen | X670, X670E, B650 |
| sTRX4 | AMD Ryzen Threadripper 3rd Gen | TRX40 |
| sTR4 | AMD Ryzen Threadripper | X399 |
2. Budget
The motherboard manufacturers design various chipsets with more or fewer features to meet different requirements and budget. The mid and high-end motherboard chipsets have more expansion slots with better overclocking and upgrade capabilities, while in entry-level ones, you can find fewer features.
- Entry-Level (Up to $100): You can get Intel’s LGA 1200, B560, H570 boards under this range with no overclocking abilities. While in AMD, you can get B450 or X370 motherboard chipset with overclocking abilities under this range.
- Mid-Range ($100-$200): Between $100-$150, you can get Intel’s B660, H760, etc., with overclocking capabilities. In AMD, you can get some other premium features like RGB lighting, WiFi cards, etc., with advanced chipsets (X570).
- High-End ($200+): You can get premium motherboard chipsets like HEDT or Intel’s Z490 and Z590 for under $200-$300. But only go for them when you have intensive gaming, content creation and multitasking needs.
3. Form Factor
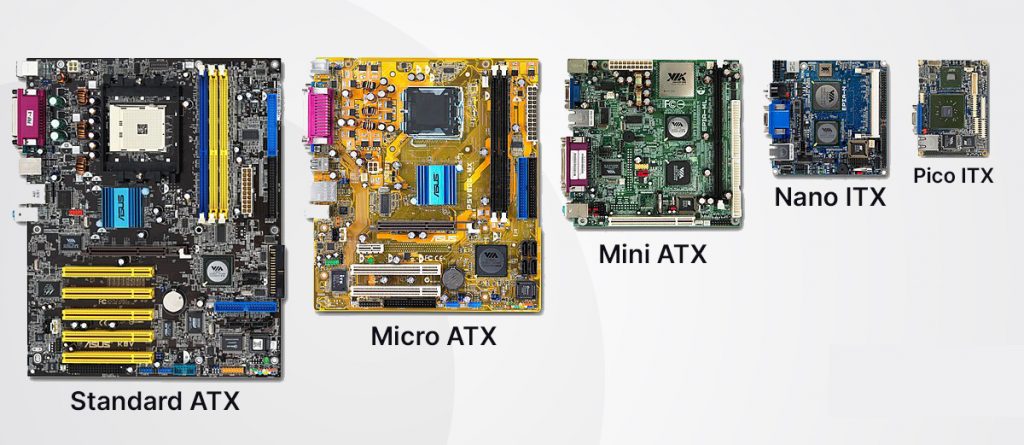
Motherboards come in three different sizes depending on what type of PC you wish to build (from micro to massive workstations) and the space you have. The motherboard form factor determines how many ports, expansion and RAM slots it will support.
The larger the size, the more slots and components it supports for high-end performance.
- Mini ITX: Smallest and most expensive. Suitable for small spaces with limited connection options and thus hard to build.
- Micro-ATX: Slightly smaller to ATX, offering similar performance but with less upgrade and expansion options available.
- ATX: Largest and most commonly used, with maximum connections. Easy to build and upgrade, and ranges from low to high price range per your needs.
| Mini-ITX | Micro-ATX | ATX | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Size | 9.0×7.5 inches | 9.6×9.6 inches | 12×9.6 inches |
| RAM Type | DIMM | DIMM | DIMM |
| Expansion Slots | 1 | 4 | 7 |
| RAM Slots | 2 | Up to 4 | Up to 8 |
| SATA Ports | Up to 6 | Up to 8 | Up to 12 |
| GPU | 1 | Up to 3 | Up to 4 |
4. RAM Slots
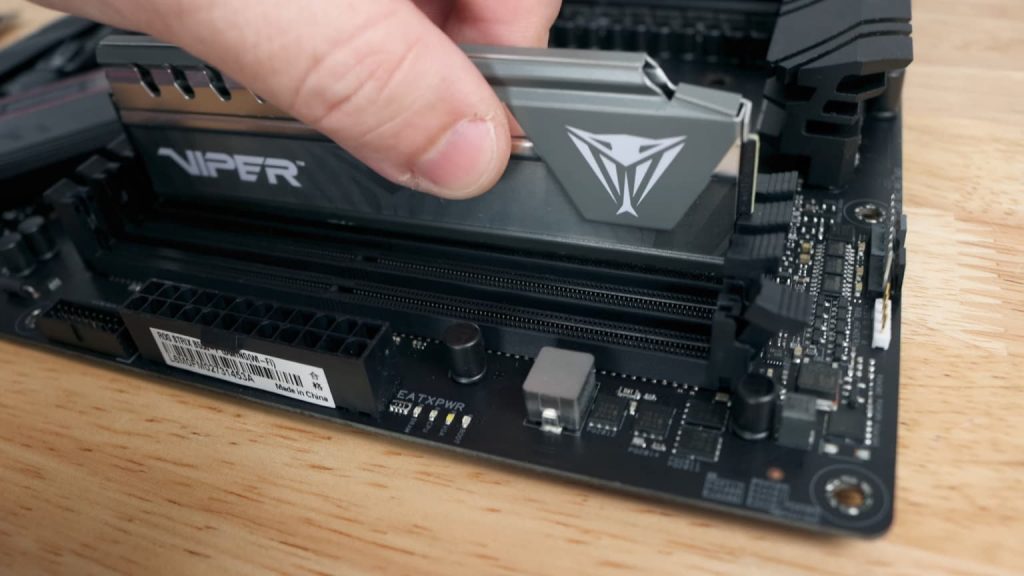

The more RAM/DIMM slots you have on your motherboard, the more RAM you can add to upgrade your system’s performance and speed. The Mini-ITX motherboard has two DIMM slots, allowing you to add up to 64GB RAM, which is more than enough for multitasking and casual gaming.
In high-end motherboards, up to 8 RAM slots are available which can be overkill. For professional gaming, graphics-intensive programs and simultaneous multitasking, four RAM slots are ideal. Depending on your needs, you can choose the right RAM for your PC by referring to this guide.
5. Expansion Slots
A motherboard must have enough PCIe or PCi slots for your GPUs, SATA, and network interface cards’ expansion. While PCIe is the latest expansion slot type available, some motherboards also have PCI slots for legacy components. Apart from PCIe, the motherboard also has some SATA slots for HDD or SATA SSD storage expansion.
The PCIe slots come in four sizes, i.e. x1, x4, x8 and x16, for different card expansions.
- PCIe x1: For SATA and USB expansion
- PCIe x4: For NVMe M.2 SSD storage expansion
- PCIe x16: For graphics cards expansion
- PCIe x8: For NVMe M.2 SSD and GPU expansion when x4 and x16 are occupied
In the latest Intel Alder Lake and Ryzen-compatible motherboards, PCIe 4.0 standard is available, doubling the bandwidth each PCIe lane carries compared to 3.0.
The amount of PCIe slots and their sizes can vary for different motherboards. The more PCIe lanes a motherboard has, the more components you can connect to presently or in future. Usually, modern motherboards have one x16 and two or more x4 PCIe slots, but the high-end ones can have more.
6. GPU Support
If you are going for a discrete GPU, check whether it is compatible with your motherboard. Also, check how many GPUs your motherboard can support if you wish to upgrade it in future for graphics-intensive programs.
You need two or more PCIe slots available on a compatible motherboard to connect two or more GPUs (called SLI in Intel and Crossfire in AMD). Also, some larger GPUs take the width of two PCIe slots. So, your motherboard must have enough PCIe slots supporting GPU expansion.
7. I/O Ports
Check what and how many I/O ports you are getting in your motherboard at the rear & front panel. Ensure your motherboard has all the essential I/O ports you need. Usually, low-budget motherboards don’t come with the latest gen USB and Ethernet ports. Still, they have enough old-standard USB ports for integrated audio, video and other peripheral connections.
Depending upon your needs, these are some I/O ports you can check in your motherboard:
- USB 2.0: Slowest USB port but sufficient for keyboard, mouse and some other peripherals.
- USB 3.0/3.1 Gen 1: Offer faster speed than USB 2.0 ports and works with almost all peripherals. In mid and high-range motherboards, you can find two or more of them with USB 2.0 ports.
- USB 3.1 or 3.2 Gen 2: Offers double bandwidth (up to 10Gbps) than USB 3.0/3/1 Gen 1 ports. You can find them only in some mid and high-end motherboards.
- USB-C: Smaller in size, they are designed for connecting newer devices and are compatible with either USB 3.1 Gen 1 or Gen 2.
- HDMI/DisplayPort: Most common ports for modern display and graphics card connections. HDMI is ideal for 1080p resolution while DisplayPorts supports up to 8k resolution.
- Ethernet: Determines maximum network speed you can get on LAN connection. Some motherboards have two or more ethernet ports for multiple data transfers. In some motherboards, there is no built-in WIFi and thus have an additional ethernet port.
- Audio Ports: There can be dedicated in and out ports or USB ports in your motherboard for headphones and microphones. Ensure it has all audio ports per your requirements.
8. Overclocking

If you are planning for overclocking, you must go for motherboards supporting it with more voltage and power supply. In Intel, only mid and high-range motherboards with the “k” suffix allow overclocking. However, in AMD, even some low-end motherboards (A#20 chipsets) support overclocking.
While the low-end motherboards can overclock, you must not use them. This is because they have insufficient power phases and a cooling system that can damage your system when drawing more voltage for overclocking.
9. Upgradeability
Some motherboards are forward compatible with the latest Gen CPU, so if you wish to upgrade, you can use the same motherboard for processors belonging to the 13th Gen or so. For your frequent upgrading requirements, ensure your motherboard has a compatible CPU socket and enough expansion slots to meet your current and future needs.
10. Aesthetics and Ease of Building

If aesthetics matter to you, go for a motherboard with RGB lights to easily see the onboard labels. Also, the USB headers, SATA ports, fans, etc., must be placed around the edges instead of sticking vertically for an easy and neat build.
For ease of build, look at how much space your motherboard has and how easily it fits all components together. Mini-ITX motherboards being the smallest in size, can be complex for beginners to build, while ATX offers more space to fit more components easily.
Frequently Asked Questions
Ideally, you should choose the CPU first according to your budget and performance requirements. Then you should look for a compatible motherboard with expansion, overclocking and upgrade abilities to meet your future needs easily.
It depends upon your usage and requirements. For normal work and casual gaming usage, a motherboard supporting 8-16GB RAM is enough. For high-end gaming, content creation, programming and multitasking needs, motherboards supporting 32-64GB RAM are good.
Yes, almost all modern motherboards come with one or more ethernet ports. However, some motherboards can even work without one. All they need is a WiFi, cellular or Bluetooth connection to connect to the networking device.
The best motherboards for gaming are the one that supports DDR4 and DDR5 RAM, with enough PCIe ports (especially x4 and x16) for the expansion of graphics cards. They must be compatible with the latest gaming chipsets, having better heatsinks and overclocking abilities for hard-core gaming performance.
Conclusion
Once you identify the kind of motherboard you require for your PC build per your requirements and budget, you must go for reputable manufacturers to pick the best one. Some of the best motherboard manufacturing brands you can consider are ASUS, MSI, Gigabyte, etc. While buying one, keep factors like final PC size, upgrade functionalities and expansion options in mind for long-term usage.
