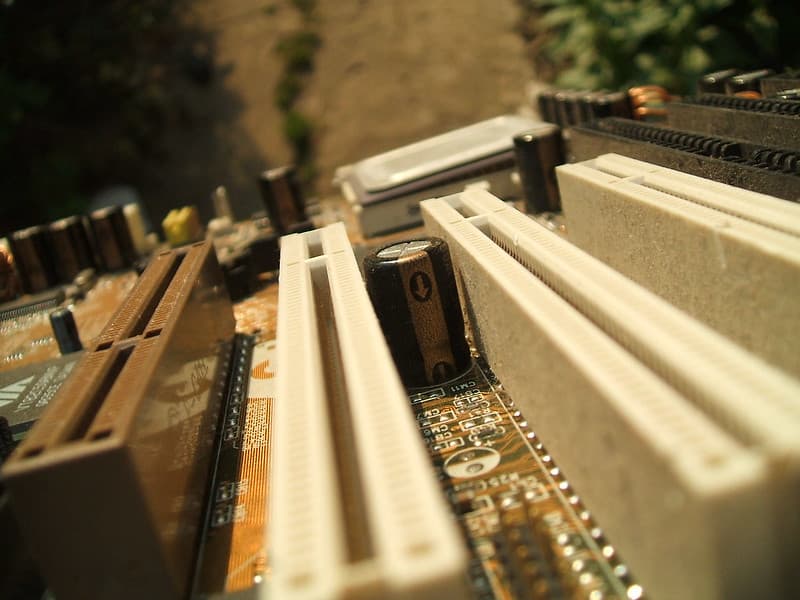
Modern motherboards come with various internal and external ports (also known as expansion slots) to add multiple audio, video, and networking functionalities. The internal ports (SATA, PCle, CPU, etc.) are majorly for RAM, Processor and Storage expansion. In contrast, the external ports let you connect useful peripherals like USB, Mouse, Keyboard or external HDD for expansion without opening the case.
Motherboard slots are designed either for a specific component or for general expansion. However, the number of expansion slots can vary in various keyboards (usually around 24 with 6 inches long each). In this guide, I will talk about all types of expansion slots in the motherboard to give you a clear picture. Check it out.
Types of Slots in Computer – Motherboard Slots Explained
Here are various types of slots you can find in a motherboard on its internal and external sides along with their functionalities:
1. CPU Slots
The CPU socket is the slot between a microprocessor and motherboard, specifically designed to connect the CPU only. To perfectly align your CPU in its socket, you must align its pin perfectly. Not all CPUs are compatible with every motherboard as there are two types of CPU sockets available on different motherboards, i.e.:
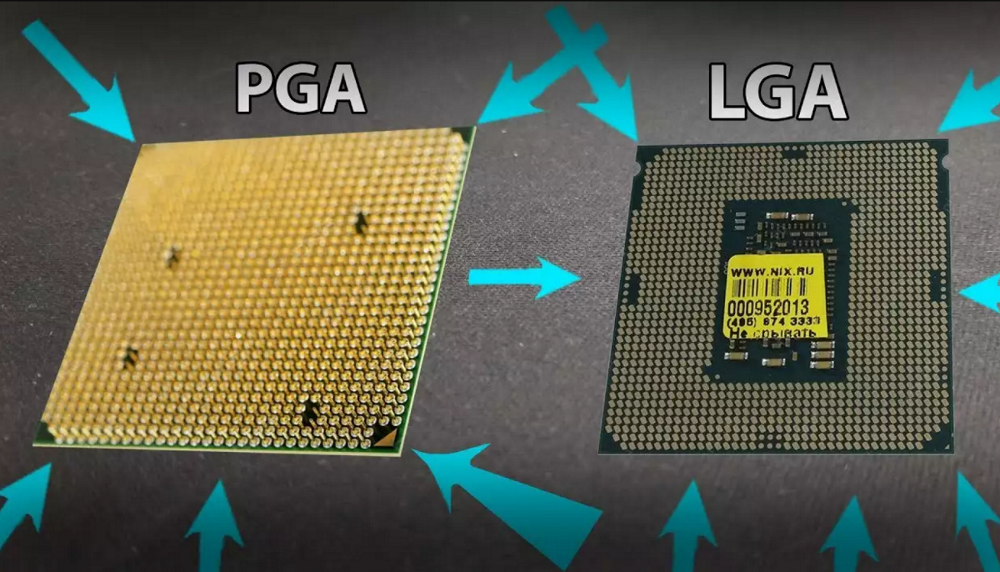
- LGA (Land Grid Array): This type of motherboard socket has female connectors or pins on it in which the processor gets plugged in.
- PGA (Pin Grid Array): It is the opposite of the LGA socket, where the pins are first connected to the processor and then plugged into the motherboard socket with appropriate holes.
Some motherboards have an additional CPU slot for expansion. If your motherboard doesn’t have it, you can use a dual-core processor (compatible with your motherboard) that uses a single CPU slot but offers more performance and processing power.
2. RAM Slot
Most motherboards have two or more RAM slots. The type and speed of RAM your system supports depend on its motherboard compatibility. The slots are designed differently to accept specific RAM types from DDR1 to DDR4.
Some RAM slots are not cross-compatible; thus you cannot use the latest RAM module in that slot. So you must check the compatibility beforehand,
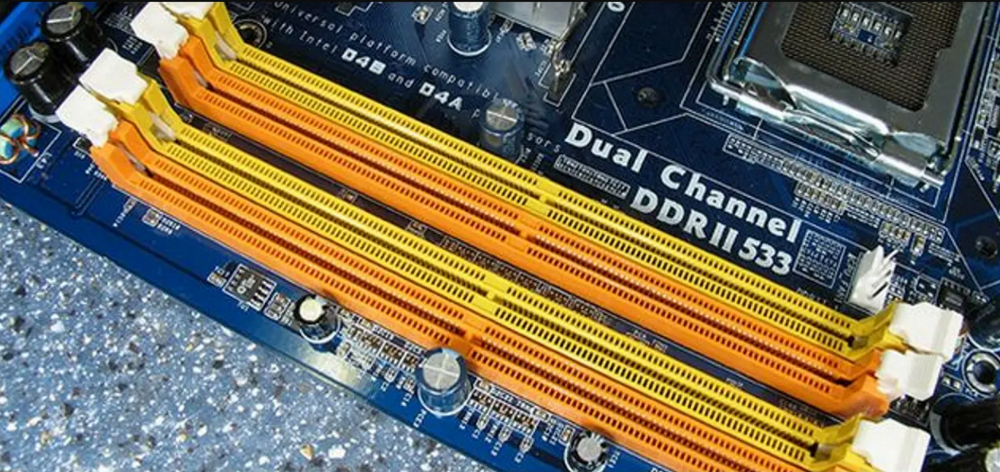

Some motherboards have dual-channel memory slots, color coded differently. In such slots, memory should be installed in pairs for optimal performance. To fit RAM perfectly in its slot, align its notch correctly with the pins on the slot until you hear a clicking sound.
3. Hard Drive Slot (SATA/PATA)
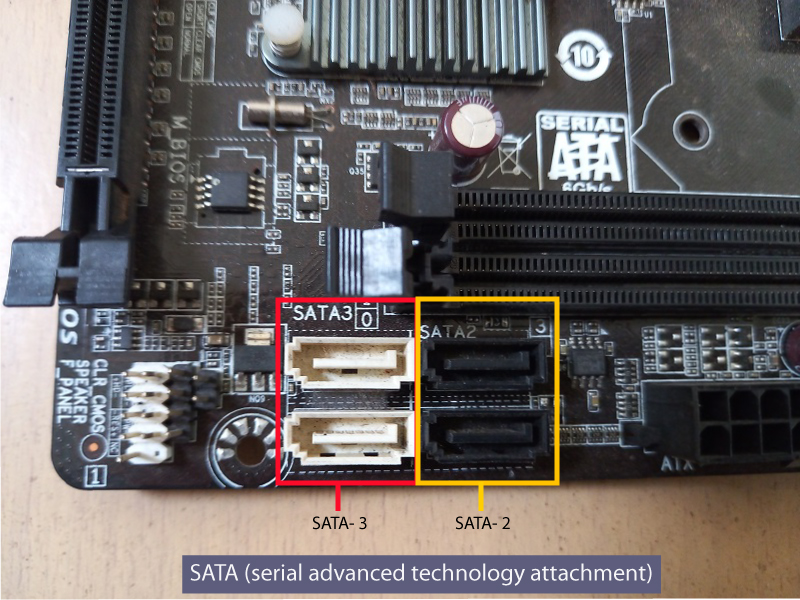
SATA (Serial Advanced Technology Attachment) is a small rectangular port on the motherboard to connect hard drives and SSD to the computer. Three types of SATA ports are available (color coded differently) to connect various SSD based on their speed types, i.e.
- SATA 1.0: Offers data transfer speed of 1.5 Gbps or 187.5 Mbps.
- SATA 2.0: Offers data transfer speed of 3 Gbps or 375 Mbps.
- SATA 3.0: Offers data transfer speed of 6 Gbps or 750 Mbps.
In older motherboards, a PATA (Parallel Advanced Technology Attachment) slot is available for connecting disk drives and CD and DVD recorders via a ribbon cable instead of SATA ports. The PATA ports resemble more like PCi or PCie ports than SATA ports.

4. PCl Slot
Stands for “Peripheral Components Interconnect”, it is the most common type of expansion slot on a Motherboard. These slots allow the peripheral components to utilize system memory directly without the CPU.
PCl slot offers parallel data transmission through its two versions, i.e. 32-bit and 64-bit, at 33 MHz and 66 Mhz clock speeds, respectively. The maximum transmission speed for the 32-bit version is 266 Mbps and 533 Mbps for the 64-bit version.
You can use various components with PCl slots, such as WiFi adapters, controllers, Network cards, Video and Audio cards, TV tuners, etc. Usually, there are two to six PCl slots available on a motherboard with a three-quarter long notch measuring from the motherboard’s outer edge. PCl Slots are generally compatible with older expansion cards, unlike its successor PCle.
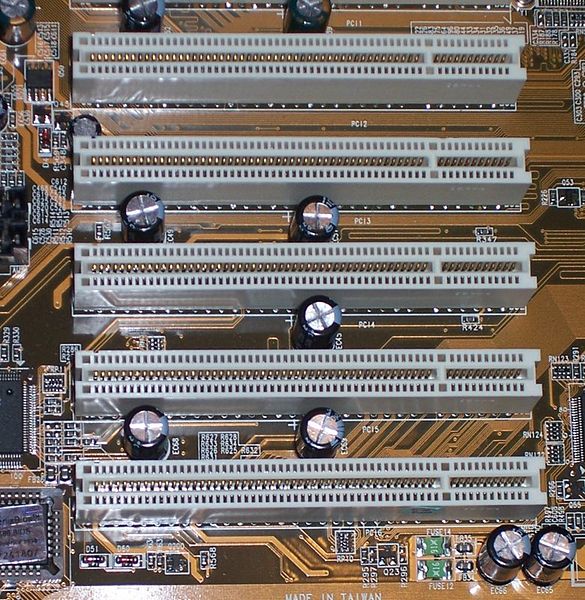

5. PCI-X Slot
The X in PCl-X stands for extended, as this slot was released to replace the conventional PCl slot for faster (four times better) clock speed. PCl-X slot is a double-wide version (working with 64-bits only) of the PCl slot.
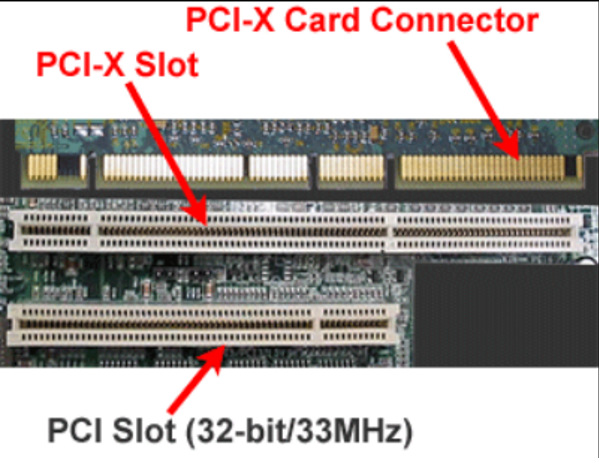
While the slot works on a similar parallel transmission protocol, it can be operated at various clock speeds, i.e. 66MHz, 100MHz, 133MHz and up to 533MHz, offering a maximum transmission speed of 1.6 Gbps.
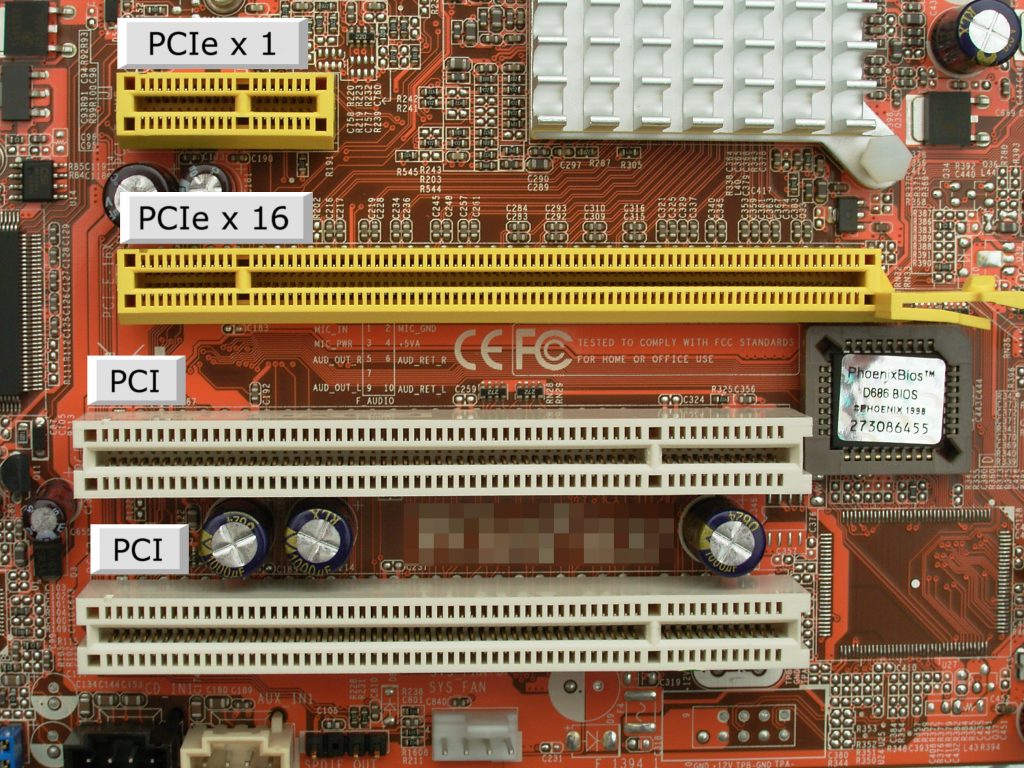
6. PCl Express (PCle) Slot
PCl Express is the successor of the PCl and PCl-X slots, offering the fastest transmission speed for peripheral components (primarily graphics cards) on the motherboard. In modern motherboards, the PCle slot has replaced the traditional AGP slot to be used as the primary slot for GPU.
It is currently the fastest expansion slot available, similar to the PCl slot but measures around one-third in length. Instead of parallel transmission, it works on serial transmission to offer maximum transmission speeds of up to 16 Gbps.
However, the size of the PCle slot can vary in a motherboard, like x1, x4, x8, x16, etc. Each number represents the number of PCle lanes the slot offers. The more lanes, the higher will be the bandwidth/transmission speed (gets doubled for each lane, as shown in a table later).
Installing the same PCI Express card in its slot is better to avoid slow performance. Although PCl and PCle slots are somewhat similar, they are not cross-compatible.
Older Expansion Slots on Motherboards
1. AGP Slot
Stands for Accelerated Graphics Port, this slot is available only in older motherboards to connect the graphics card for accelerating 3D output. AGP offers faster and better throughput than PCI, but in the high-end motherboards, this slot is replaced by PCI express slot for higher bandwidth.
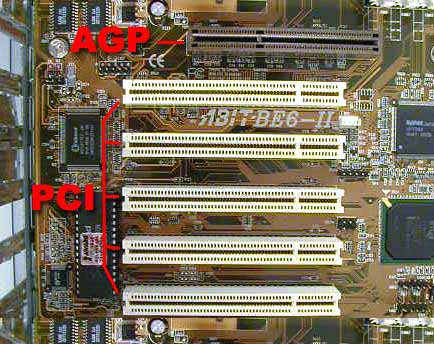
2. ISA Slot
ISA (Industry Standard Architecture) is the oldest expansion slot for older (8-bit and 16-bit compatible) PCs. It is compatible only with older expansion cards; thus, most modern motherboards usually don’t have it.
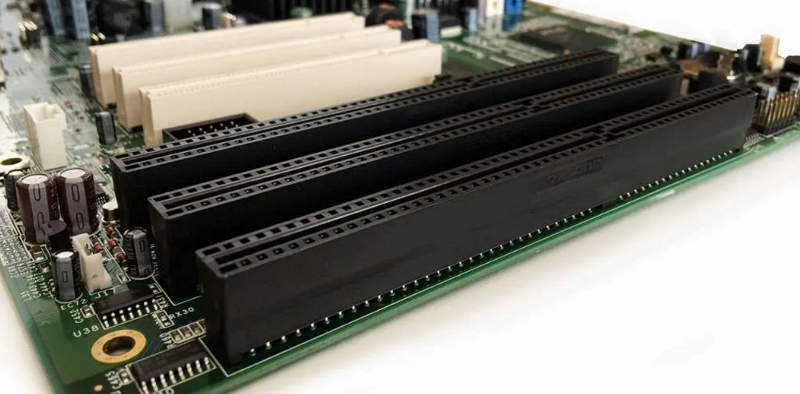
3. EISA Slot
Stands for Extended Industry Standard Architecture, the EISA slot is the modern version of the ISA slot, offering better and faster bus speed with 32-bit Direct Memory Access. These slots are cross-compatible with ISA and designed for Network Interface Cards.
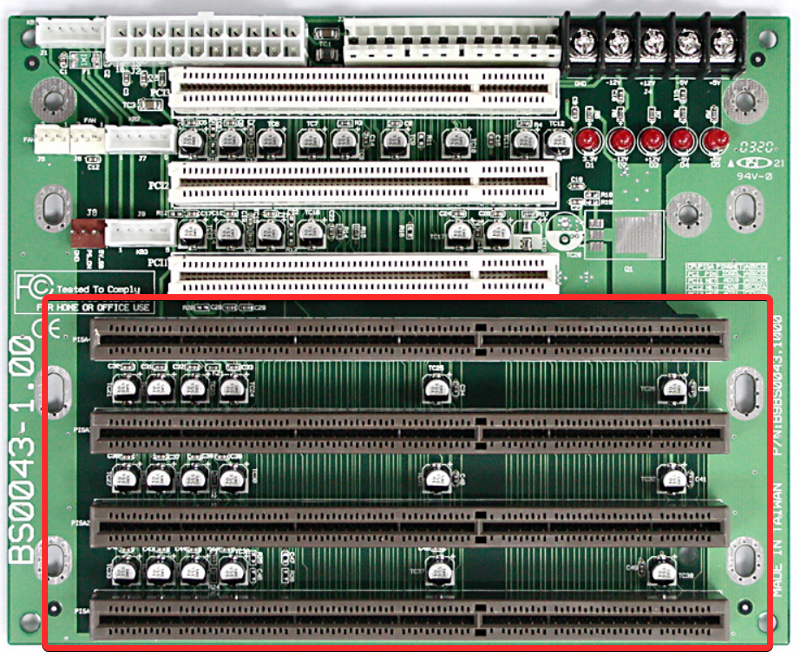
Modern motherboards can have five (or more) built-in EISA slots with configurations ranging from 1x to 16x, where x represents the number of cards you can insert in one slot.
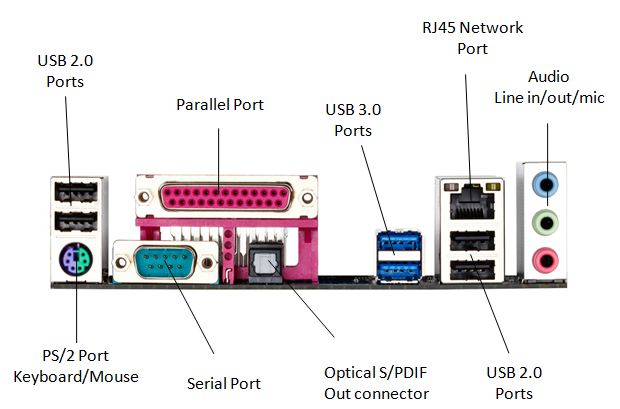
4. External/Rear Motherboard Ports
- Ethernet/RJ-45 Port: Use for wired connections
- USB Port: For connecting USB peripherals like keyboard, mouse, HDD, etc.
- HDMI/VGA/DisplayPort: Display connectors for offering video or audio output to the monitor
- Analog/Digital Audio Port: Sound connector for digital audio equipment and speakers.
- Parallel Port: Allow connecting printer and other peripheral components to the system via the parallel interface.
- Serial Port: Let you connect a serial device to the PC for transmitting data one bit at a time.
Bandwidth of Different Slot Types
| Slot Type | Bandwidth |
|---|---|
| AGP 8x | 2100 Mbps |
| PCl | 132 Mbps |
| PCl Express 1x | 250 Mbps in a single direction, 500 Mbps in two directions |
| PCl Express 2x | 500 Mbps in a single direction, 1000 Mbps in two directions |
| PCl Express 4x | 1000 Mbps in a single direction, 2000 Mbps in two directions |
| PCl Express 8x | 2000 Mbps in a single direction, 4000 Mbps in two directions |
| PCl Express 16x | 4000 Mbps in a single direction, 8000 Mbps in two directions |
| PCl Express 32x | 8000 Mbps in a single direction, 16 Gbps in two directions |
| USB 2.0 | 60 Mbps |
| Gigabit Ethernet | 125 Mbps |
Types of Expansion Cards
An expansion card is inserted into the motherboard’s expansion slots for additional functionality. Depending upon the functionality you wish to add to your PC, you can buy an expansion card separately. Here are some of the common ones:
1. Sound Card
For adding all types of audio data capabilities to your PC.
2. Video Card
Provides High-Definition Video output for video editing, multimedia, gaming and entertainment purposes.
3. NIC Card
Also known as a network or LAN adapter for connecting a PC to the computer network. It has ethernet ports on it that can be attached to an RJ-45 connector on the PC.
4. WiFi Card
Adds wireless capabilities to the PCs that lack them so they can access WiFi signals. This card has a small external antenna for sending and receiving signals.
5. USB card
Allow to add more USB connections to the PC.
6. Modem card
This card is used to add in older PCs for converting analog signals to digital but comes built-in in the latest motherboards.
7. Storage Card
Allow you to connect SSD, Flash Drive or SD card storage to the PC.
8. Interface Card
This card has multiple ports on it for various connection types like SATA, USB, HDMI, etc.
9. TV Card
It adds functionality to convert your PC into a TV and is suitable for those who don’t have a digital computer.
Frequently Asked Questions
There are three types of GPU slots available: PCI, AGP and PCIe. While PCI and AGP are usually found on older motherboards with less bandwidth, PCIe is the fastest and most common GPU slot, offering a maximum transmission speed of up to 16Gbps.
Slot-1 is the 242-pin slot on the motherboard, introduced by Intel to connect its CPU modules, like Celeron, Pentium Pro, Pentium 2, and Pentium 3, similar to an expansion card.
A2 and B2 are the RAM Slots 2 and 4, respectively and are considered the dual-RAM channel slots. For a single RAM stick, an A2 slot is used, while for two RAM sticks, A2 and B2 are used. If there is a third RAM stick, it is placed between A2 and B2.
Three types of expansion slots available on modern motherboards are PCI, PCI Express and AGP. On some high-end motherboards, AGP is replaced by PCI for primary graphics card expansion as it offers better output and bandwidth.
Conclusion
Over time, expansion and other slots on PC and motherboards evolved significantly. Thus, depending on which motherboard you have, the slots mentioned above can vary slightly. But you can always use expansion cards in your motherboard’s expansion slot to add more functionalities if your system lacks them or you want to upgrade them.
